In situations where you’re not involved in the data gathering process (primary research), you have to rely on existing information and data to arrive at specific research conclusions or outcomes. This approach is known as secondary research.
In this article, we’re going to explain what secondary research is, how it works, and share some examples of it in practice.
What is secondary research?
Secondary research, also known as desk research, is a research method that involves compiling existing data sourced from a variety of channels. This includes internal sources (e.g.in-house research) or, more commonly, external sources (such as government statistics, organisational bodies, and the internet).
Secondary research comes in several formats, such as published datasets, reports, and survey responses, and can also be sourced from websites, libraries, and museums.
The information is usually free — or available at a limited access cost — and gathered using surveys, telephone interviews, observation, face-to-face interviews, and more.
When using secondary research, researchers collect, verify, analyse and incorporate it to help them confirm research goals for the research period.
As well as the above, it can be used to review previous research into an area of interest. Researchers can look for patterns across data spanning several years and identify trends — or use it to verify early hypothesis statements and establish whether it’s worth continuing research into a prospective area.
How to conduct secondary research
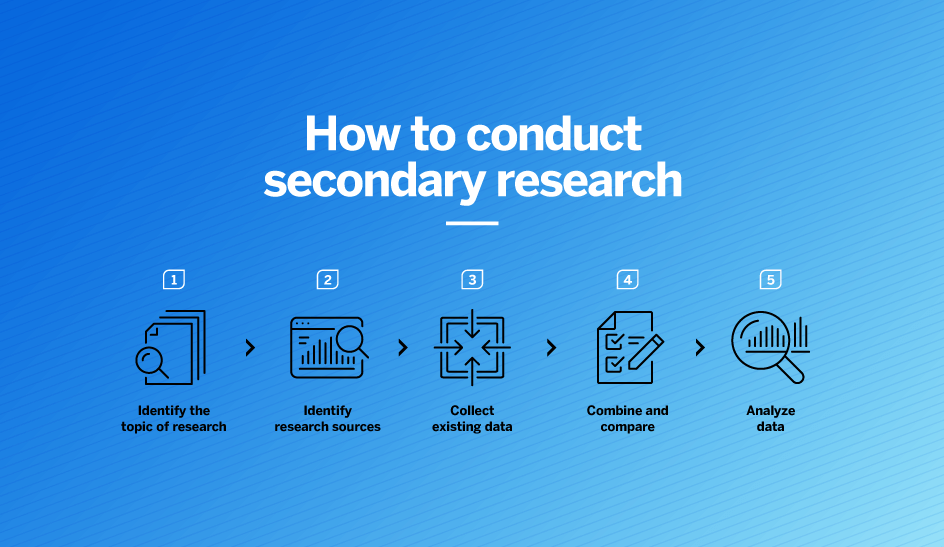
There are five key steps to conducting secondary research effectively and efficiently:
1. Identify and define the research topic
First, understand what you will be researching and define the topic by thinking about the research questions you want to be answered.
Ask yourself: What is the point of conducting this research? Then, ask: What do we want to achieve?
This may indicate an exploratory reason (why something happened) or confirm a hypothesis. The answers may indicate ideas that need primary or secondary research (or a combination) to investigate them.
2. Find research and existing data sources
If secondary research is needed, think about where you might find the information. This helps you narrow down your secondary sources to those that help you answer your questions. What keywords do you need to use?
Which organisations are closely working on this topic already? Are there any competitors that you need to be aware of?
Create a list of the data sources, information, and people that could help you with your work.
3. Begin searching and collecting the existing data
Now that you have the list of data sources, start accessing the data and collect the information into an organised system. This may mean you start setting up research journal accounts or making telephone calls to book meetings with third-party research teams to verify the details around data results.
As you search and access information, remember to check the data’s date, the credibility of the source, the relevance of the material to your research topic, and the methodology used by the third-party researchers. Start small and as you gain results, investigate further in the areas that help your research’s aims.
4. Combine the data and compare the results
When you have your data in one place, you need to understand, filter, order, and combine it intelligently. Data may come in different formats where some data could be unusable, while other information may need to be deleted.
After this, you can start to look at different data sets to see what they tell you. You may find that you need to compare the same datasets over different periods for changes over time or compare different datasets to notice overlaps or trends. Ask yourself: What does this data mean to my research? Does it help or hinder my research?
5. Analyse your data and explore further
In this last stage of the process, look at the information you have and ask yourself if this answers your original questions for your research. Are there any gaps? Do you understand the information you’ve found? If you feel there is more to cover, repeat the steps and delve deeper into the topic so that you can get all the information you need.
If secondary research can’t provide these answers, consider supplementing your results with data gained from primary research. As you explore further, add to your knowledge and update your findings. This will help you present clear, credible information.
Primary vs secondary research
Unlike secondary research, primary research involves creating data first-hand by directly working with interviewees, target users, or a target market. Primary research focuses on the method for carrying out research, asking questions, and collecting data using approaches such as:
- Interviews (panel, face-to-face or over the phone)
- Questionnaires or surveys
- Focus groups
Using these methods, researchers can get in-depth, targeted responses to questions, making results more accurate and specific to their research goals. However, it does take time to do and administer.
Unlike primary research, secondary research uses existing data, which also includes published results from primary research. Researchers summarise the existing research and use the results to support their research goals.
Both primary and secondary research have their places. Primary research can support the findings found through secondary research (and fill knowledge gaps), while secondary research can be a starting point for further primary research. Because of this, these research methods are often combined for optimal research results that are accurate at both the micro and macro level.
| Primary Research | Secondary Research |
| First-hand research to collect data. May require a lot of time | The research collects existing, published data. May require a little time |
| Creates raw data that the researcher owns | The researcher has no control over data method or ownership |
| Relevant to the goals of the research | May not be relevant to the goals of the research |
| The researcher conducts research. May be subject to researcher bias | The researcher collects results. No information on what researcher bias existsSources of secondary research |
| Can be expensive to carry out | More affordable due to access to free data |
Sources of Secondary Research
There are two types of secondary research sources: internal and external. Internal data refers to in-house data that can be gathered from the researcher’s organisation. External data refers to data published outside of and not owned by the researcher’s organisation.
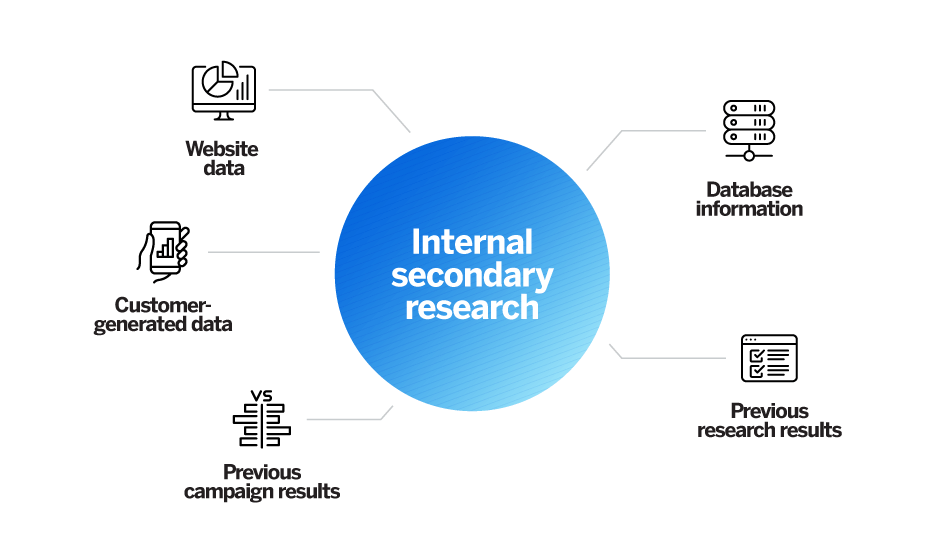
Internal data
Internal data is a good first port of call for insights and knowledge, as you may already have relevant information stored in your systems. Because you own this information — and it won’t be available to other researchers — it can give you a competitive edge. Examples of internal data include:
- Database information on sales history and business goal conversions
- Information from website applications and mobile site data
- Customer-generated data on product and service efficiency and use
- Previous research results or supplemental research areas
- Previous campaign results
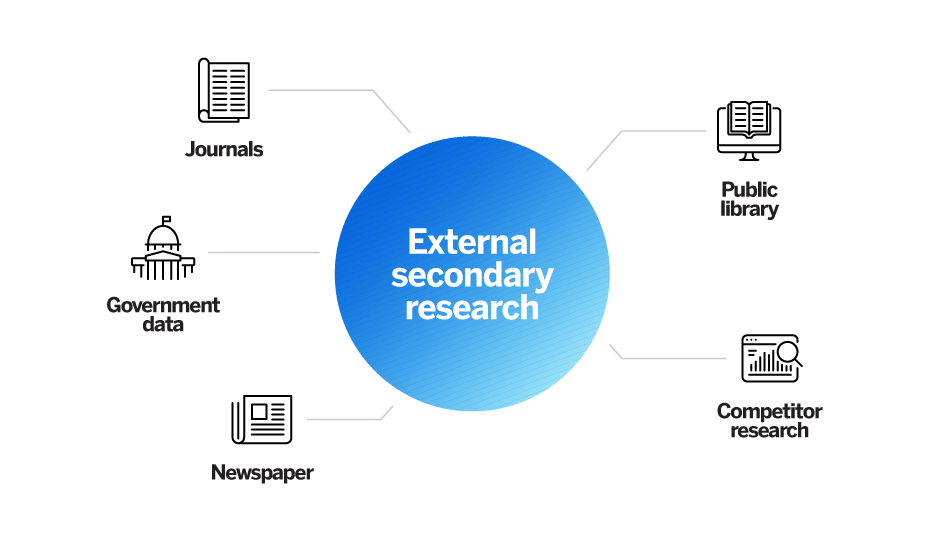
External data
External data is useful when you: 1) need information on a new topic, 2) want to fill in gaps in your knowledge, or 3) want data that breaks down a population or market for trend and pattern analysis. Examples of external data include:
- Government, non-government agencies, and trade body statistics
- Company reports and research
- Competitor research
- Public library collections
- Textbooks and research journals
- Media stories in newspapers
- Online journals and research sites
Three examples of secondary research methods in action
How and why might you conduct secondary research? Let’s look at a few examples:
1. Collecting factual information from the internet on a specific topic or market
There are plenty of sites that hold data for people to view and use in their research. For example, Google Scholar, ResearchGate, or Wiley Online Library all provide previous research on a particular topic. Researchers can create free accounts and use the search facilities to look into a topic by keyword, before following the instructions to download or export results for further analysis.
This can be useful for exploring a new market that your organisation wants to consider entering. For instance, by viewing the U.S Census Bureau demographic data for that area, you can see what your target audience’s demographic segmentations are, and create compelling marketing campaigns accordingly.
2. Finding out the views of your target audience on a particular topic
If you’re interested in seeing the historical views on a particular topic, for example, attitudes to women’s rights in the US, you can turn to secondary sources.
Textbooks, news articles, reviews, and journal entries can all provide qualitative reports and interviews covering how people discussed women’s rights. There may be multimedia elements like video or documented posters of propaganda showing biased language usage.
By gathering this information, synthesising it, and evaluating the language, who created it and when it was shared, you can create a timeline of how a topic was discussed over time.
3. When you want to know the latest thinking on a topic
Educational institutions, such as schools and colleges, create a lot of research-based reports on younger audiences or their academic specialisms. Dissertations from students also can be submitted to research journals, making these places useful places to see the latest insights from a new generation of academics.
Information can be requested — and sometimes academic institutions may want to collaborate and conduct research on your behalf. This can provide key primary data in areas that you want to research, as well as secondary data sources for your research.
Advantages of secondary research
There are several benefits of using secondary research, which we’ve outlined below:
- Easily and readily available data – There is an abundance of readily accessible data sources that have been pre-collected for use, in person at local libraries and online using the internet. This data is usually sorted by filters or can be exported into spreadsheet format, meaning that little technical expertise is needed to access and use the data.
- Faster research speeds – Since the data is already published and in the public arena, you don’t need to collect this information through primary research. This can make the research easier to do and faster, as you can get started with the data quickly.
- Low financial and time costs – Most secondary data sources can be accessed for free or at a small cost to the researcher, so the overall research costs are kept low. In addition, by saving on preliminary research, the time costs for the researcher are kept down as well.
- Secondary data can drive additional research actions – The insights gained can support future research activities (like conducting a follow-up survey or specifying future detailed research topics) or help add value to these activities.
- Secondary data can be useful pre-research insights – Secondary source data can provide pre-research insights and information on effects that can help resolve whether research should be conducted. It can also help highlight knowledge gaps, so subsequent research can consider this.
- Ability to scale up results – Secondary sources can include large datasets (like Census data results across several states) so research results can be scaled up quickly using large secondary data sources.
Disadvantages of secondary research
The disadvantages of secondary research are worth considering in advance of conducting research:
- Secondary research data can be out of date – Secondary sources can be updated regularly, but if you’re exploring the data between two updates, the data can be out of date. Researchers will need to consider whether the data available provides the right research coverage dates, so that insights are accurate and timely, or if the data needs to be updated. Also, fast-moving markets may find secondary data expires very quickly.
- Secondary research needs to be verified and interpreted – Where there’s a lot of data from one source, a researcher needs to review and analyse it. The data may need to be verified against other data sets or your hypotheses for accuracy and to ensure you’re using the right data for your research.
- The researcher has had no control over the secondary research – As the researcher has not been involved in the secondary research, invalid data can affect the results. It’s therefore vital that the methodology and controls are closely reviewed so that the data is collected in a systematic and error-free way.
- Secondary research data is not exclusive – As data sets are commonly available, there is no exclusivity and many researchers can use the same data. This can be problematic where researchers want to have exclusive rights over the research results and risk duplication of research in the future.
When do we conduct secondary research?
Now that you know the basics of secondary research, when do researchers normally conduct secondary research?
It’s often used at the beginning of research, when the researcher is trying to understand the current landscape. In addition, if the research area is new to the researcher, it can form crucial background context to help them understand what information exists already. This can plug knowledge gaps, supplement the researcher’s own learning or add to the research.
Secondary research can also be used in conjunction with primary research. Secondary research can become the formative research that helps pinpoint where further primary research is needed to find out specific information. It can also support or verify the findings from primary research.
You can use secondary research where high levels of control aren’t needed by the researcher, but a lot of knowledge on a topic is required from different angles.
Secondary research should not be used in place of primary research as both are very different and are used for various circumstances.
Questions to ask before conducting secondary research
Before you start your secondary research, ask yourself these questions:
- Is there similar internal data that we have created for a similar area in the past?
If your organisation has past research, it’s best to review this work before starting a new project. The older work may provide you with the answers, and give you a starting dataset and context of how your organisation approached the research before. However, be mindful that the work is probably out of date and view it with that note in mind. Read through and look for where this helps your research goals or where more work is needed.
- What am I trying to achieve with this research?
When you have clear goals, and understand what you need to achieve, you can look for the perfect type of secondary or primary research to support the aims. Different secondary research data will provide you with different information – for example, looking at news stories to tell you a breakdown of your market’s buying patterns won’t be as useful as internal or external data e-commerce and sales data sources.
- How credible will my research be?
If you are looking for credibility, you want to consider how accurate the research results will need to be, and if you can sacrifice credibility for speed by using secondary sources to get you started. Bear in mind which sources you choose — low-credibility data sites, like political party websites that are highly biased to favour their own party, would skew your results.
- What is the date of the secondary research?
When you’re looking to conduct research, you want the results to be as useful as possible, so using data that is 10 years old won’t be as accurate as using data that was created a year ago. Since a lot can change in a few years, note the date of your research and look for earlier data sets that can tell you a more recent picture of results. One caveat to this is using data collected over a long-term period for comparisons with earlier periods, which can tell you about the rate and direction of change.
- Can the data sources be verified? Does the information you have check out?
If you can’t verify the data by looking at the research methodology, speaking to the original team or cross-checking the facts with other research, it could be hard to be sure that the data is accurate. Think about whether you can use another source, or if it’s worth doing some supplementary primary research to replicate and verify results to help with this issue.
What next?
We created a front-to-back guide on conducting market research, The ultimate guide to conducting market research, so you can understand the research journey with confidence.
In it, you’ll learn more about:
- What effective market research looks like
- The use cases for market research
- The most important steps to conducting market research
- And how to take action on your research findings
Download the free guide for a clearer view on secondary research and other key research types for your business.
Download our free guide for a clearer view on market research for your business